Loopring Price Analysis: Version 3.0 releases
Loopring's decentralized protocol solution hit a major milestone in early May with the launch of version 3.0 - adding off-chain based scaling and fee optimization using zk-SNARKS. Technical indicators lean bearish, however, and LRC's price in the short term remains in the hand of speculators and not users.
Loopring (LRC) is an open-source protocol for building decentralized exchanges. It functions as a set of smart contracts that verify tradeable orders. The protocol performs trade settlement on-chain while keeping all order management off-chain. Loopring works by pooling all orders sent to its networks and filling these orders using the order books of multiple decentralized exchanges. The Loopring protocol operates as a sidechain of the Ethereum network.
Loopring’s native LRC token is currently trading at ~$0.055 and is ranked 107th on Brave New Coin’s market cap table. It has dropped ~7% in the last week and ~27% in the last month. The price of LRC has increased 78% after bottoming in mid-December, at the bottom of the crypto bear market.
Source: Brave New Coin
These gains have centered around two sharp price increases in late January and early April. The jump in January appears to have been algorithmically driven with a number of other altcoins (REP, POWR, SNT) spiking at similar time frames on the Binance exchange. The spike in early April appears to have been led by the overall crypto market, with a strong move up around those dates.
The high volatility of LRC in recent months suggests a small, immature, marketplace driven by speculation. As the Loopring protocol develops, price discovery will improve due to external factors like improved Ethereum network monitoring tools. This will help reduce volatility levels.
The Loopring protocol is blockchain agnostic and can be deployed on any blockchain with smart contract capability. Last year Loopring released Loopring NEO and the LRN token designed to finalize and run trading systems on the NEO network.
However, Loopring NEO had challenges delivering a workable NEO DEX solution. In a Reddit AMA, Loopring founder Daniel Wan explained that the "issue with the NEO platform is that the cost (gas assumption) of both deploying the protocol and settlement of even the most straightforward ring of two orders is too high; thus there is no way to put such a protocol into production."
In its 2019 roadmap, the Loopring Foundation announced plans to launch ‘Loopring Chain’, an application-specific side-chain exclusively used for Loopring protocol orders. The Loopring Chain will be an Ethereum compatible, public side-chain, and will allow ERC-20 tokens to be exchanged between the two chains 1:1, without trust. LRN will have utility on the Loopring chain once it is launched.
The Loopring solution aims to provide low fees, liquidity, transparency, and security, challenging some of the inherent issues within both centralized and decentralized crypto exchange models.
Loopring organizes trade orders by using a unidirectional order model (UDOM). In this format, trades are formatted as "exchange requests", where there is no price in a common currency as per normal trading systems, but instead a direct exchange of tokens. Users remain in control of their own keys and funds throughout the exchange process.
For example, a quote could be presented as 1000 LRC for 1 ETH. Loopring collects quotes to create an order-ring matching system that allows disparate trading pairs to be stitched together in a circular trade. Unique base/quote orders are mixed between pairs in a ring, expanding potential liquidity by increasing the number of potential trading counterparties. In this example, the 1 ETH could be filled with an ETH for WBTC (Wrapped Bitcoin) order via communication within the order ring. Orders in a ring don’t need to be fully matched, in the earlier example, the 1 ETH could have been filled with an order selling 3 ETH for WBTC, with the 2nd order, if unable to be filled fully, being sent to the next order ring to find a liquidity partner to fully complete the order to satisfaction.
To begin the transaction process, a trader makes an order from a Loopring protocol supported blockchain wallet or DEX. The order is then sent to a meshed network of relays. The relays then update their orders and communicate with each other to match orders and find the best exchange orders. Ring miners then organize trades into single order rings and run matching order algorithms in order to submit them to the smart contract for execution. The Loopring smart contract then executes matching trades, swaps the tokens between the respective traders, and pays fees to wallets. A user can be both a ring miner and a relay within Loopring.
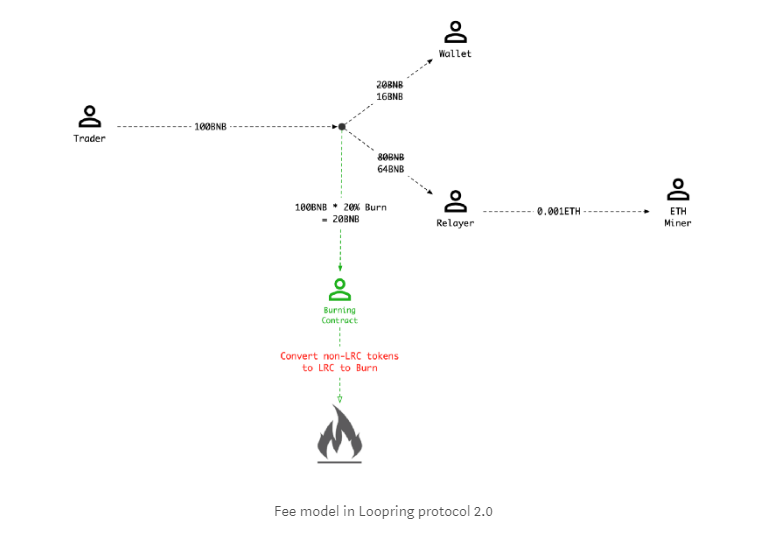
Each facilitator in the Loopring protocol; the wallet, relayer, ring miner, and the smart contract, are paid for their services. Traders pay a transaction fee to wallets/DEXs and to the ring miners for their services, with ring miners generally earning a higher share. The ring miner then pays the Ethereum miner’s gas.
Due to the lack of demand for the LRC token, Loopring recently restructured the network fee system and utility of the LRC token.
On the 7th of May 2019, the Loopring protocol entered the next key phase in its product development lifecycle with the launch of Loopring 3.0 and a new ERC-20 smart contract protocol.
Loopring 3.0 increases network throughput and decreases transaction fees by increasing the number of operations that occur on-chain within the exchange protocol. Loopring compensates for a potential loss of decentralization and censorship resistance by implementing zk-SNARK technology into off-chain interactions.
zk-SNARK (Zero Knowledge-Succinct Non-Interactive Argument of Knowledge) technology is derived from zero-knowledge proofs, a type of proof-of-construction where an individual can provide proof of information without revealing the information itself. For example, zk-SNARKs let user A prove to user B that the hash value of a random number existed, without revealing what the random number was.
Using zero-knowledge protocols a DEX or wallet owner can prove that the user has sufficient balance in their account, have settled trades before final trades to miners, and other key DEX operations, off-chain. This means not inducing gas costs, and increasing the scalability of the network without sacrificing security.
The model streamlines elements of the existing Loopring DEX protocol by scooping up blocks of previously on-chain confirmation operations and handling them off-chain, before eventual final verification on the Ethereum blockchain.
In Loopring 3.0, previously on-chain stored data is now stored off-chain in a Merkle tree and then used in zk-SNARKS as required, updating the tree. The now off-chain DEX related work is packaged into blocks and instituted as multiple changes into the Merkle tree as transaction settlements when executed. The validity of this DEX related work in a block needs to be proven and submitted to the Ethereum blockchain. This is done by creating a zero-knowledge proof and confirming it on-chain.
Loopring says the new zk-SNARK based Loopring 3.0 will increase trade speeds and the efficiency of on-chain activity tenfold.
Implementing zk-SNARKS adds significant hardware requirements to Zcash transactions, and this has affected third party support for ZK-Snark Zcash addresses. Supporting Loopring 3.0 will require extra processing power requirements for exchanges and wallets.
Vitalik Buterin describes the data availability problem as where a malicious miner publishes a block where the blockheader is present but some or all of the block data is missing. Data availability protocols mitigate these occurrences.
The new Loopring supports the modified version of the network’s native LRC token. The new LRC token has radically redefined utility. Previously it functioned as a currency style token used to pay transaction fees on Loopring DEXs, now it has more of a store of value/membership style value proposition directly growing in value as the Loopring protocol is used more.
Before Loopring 2.0 was launched in late December 2018, all network fees were paid in LRC, but now in addition to LRC, traders can pay trading fees in ERC-20 tokens and WETH (wrapped, smart contract compliant ETH).
Additionally, for every trading fee payment, a cut is taken and an equivalent amount of LRC (owned by the Loopring Foundation) is burnt by the Loopring smart contract.
The Loopring 2.0 model is designed so that traders who pay for trading fees with LRC pay the lowest rates. Transaction fees paid in LRC also burn the fewest tokens. Traders and ring miners can lock LRC for access to cheaper fees and greater fee percentage retention.
Due to these factors, there are now greater incentives to accumulate LRC because it is now a ‘scarce’ resource that reduces in supply, as network activity grows.
The price and volume of LRC have picked up since January 2019. This is most visible on key altcoin exchanges like Binance. The ~78% price rise since mid-December is a bullish flag that the LRC token value restructuring may be working as intended, and buyers may be accumulating.
The new versions of LRC and the Loopring protocol come with a new decentralized exchange, Oedax. Oedax settles and finds a price based on an open Dutch auction model. The Dutch auction model is ideal for decentralized exchanges because they are bidirectional (multiple traders all interacting with each simultaneously). Smart contracts mitigate the need for a central authority to provide management and settlement.
Fundamental indicators
Loopring is one of three Ethereum DEX protocol/swap solutions, along with 0x and the Kyber network. Each uses a network of liquidity providers and relayers to ensure that classic DEX issues of long wait times and slippage are reduced.
The Loopring network’s native token LRC is the least used for on-chain operations. Through most of 2019 the transaction count for the LRC token has been between 50-150 transactions a day, compared to around 800-1,300 with ZRX and 700-1000 with KNC.
Source: Coinmetrics.io community data. LRC- Turquoise, KNC- Green, ZRX- Red. Note that the transaction count for LRC hit +80,000 on one day over the Ethereum mainnet during October 2018. This appears to have been an outlier/anomaly.
Dapp aggregator Stateofthedapps tracks the main Loopring smart contract as a single Dapp and lists it as the 101st most popular Dapp in the ecosystem. 0x and Kyber Network are the 16th and 18th most popular, respectively. Over the last month, the protocol has averaged ~42 daily active users, while 0x and Kyber network have an average of ~430 and ~194 users respectively.
In both Dapp usage and network activity, Loopring and LRC is behind its direct competitors. As DEX usage increases there may be room for all three solutions to exist within the Ethereum ecosystem in the future.
For example, Loopring’s unique, barteresque pricing model, which removes traditional market makers and takers with the ring matching model, creates more generalized pricing that may appeal to users seeking a flat marketplace. 0x resembles a more traditional exchange with an order book and is likely more suited to traders who seek to speculate on digital assets using traditional trading strategies.
More users may begin to use the platform as the infrastructure designed to connect with the Ethereum ecosystem improves and the wider Dapp ecosystem matures.
Source: Stateofthedapps.com
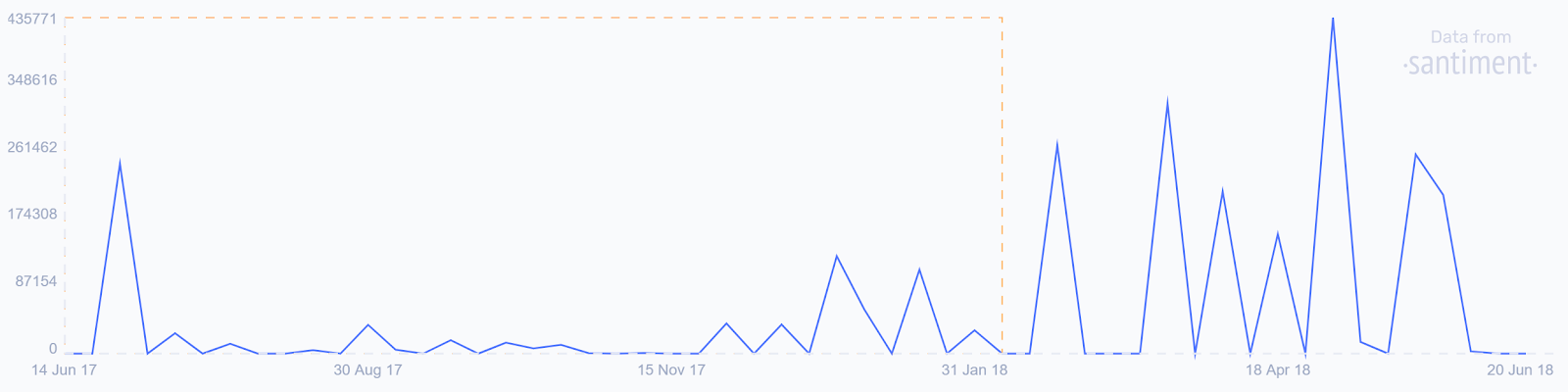
Source: Sanbase, development activity- purple dotted line
A bullish flag is a new surge in development activity of the Loopring protocol.
Most blockchain projects use the developer community GitHub, where files are saved in folders called "repositories" or "repos”. Changes to these files are recorded with "commits" which save a record of what changes were made, when, and by who. Although commits represent quantity and not necessarily quality, a higher number of commits can signify higher dev activity and interest.
The development activity score (combines the number of Github events like pulls, commits, and wiki edits) of Loopring has increased by 500% since the start of May. Much of this activity can be attributed to the release of Loopring 3.0 on the 7th of May.
The development of the Loopring protocol, the zk-SNARK off-chain data solution, and the reconfigured LRC token utility, suggests that the product team is competent and trying to find ways to create alpha within the DEX protocol space. Much of this development activity has taken place during the bear market.
Onchain cycle indicators
Derived from the NVT ratio, the NVT signal is a responsive blockchain valuation metric developed by Willy Woo and Dmitriy Kalichkin.
Crypto markets are prone to bubbles of speculative purchasing that don’t reflect underlying network fundamentals. The NVT signal provides insight into what stage of this price cycle a token may be at.
A high NVT signal is indicative of a network that is going through one of these bubble periods and may move towards a position of becoming overbought/overvalued, as the market’s speculative momentum slows.
In the short term, on-chain volume indications lean bullish for LRC. While it appears that the NVT signal is rising, the price remains stagnant and trending slightly down over the last month. It is well below an inflection level. The LRC NVT signal currently sits at ~100 points and oversold inflection levels have tended to be around 300-400 points.
This means that any speculative price momentum has room to push the price upwards before fundamental pressure kicks in, and puts downward pressure on price. Over the last week, the bitcoin markets have boomed, while altcoins have only posted mild gains against the dollar, but fallen against BTC.
Generally, altcoin price increases follow BTC price increases. This is because traders diversify a portion of their profits earned from trading bitcoin. Alts provide traders with a new avenue for high yield, when price appreciation in BTC slows down.
With the NVT signal being well below overbought levels, and the previous pumping of the LRC/BTC market on Binance, this suggests that if the crypto markets keep pushing forward, eventual gains in USD and BTC terms may materialize.
PMR signal
Metcalfe’s law is a measure of connections in a network, as established by Robert Metcalfe, the founder of Ethernet. It has subsequently been used to analyze the true value of network-based financial products like Facebook and Bitcoin. By comparing it to price, it can provide a useful tool to assess whether a token is over or undervalued.
It is also a more straightforward metric to assess when compared to on-chain transaction volume, which can be challenging to measure accurately in USD terms. Addresses are measured as the number of unique sending and receiving addresses participating in transactions daily.
Since early 2018, the LRC Metcalfe’s law value has been extremely low when compared to token value (PMR), ranging between 6-8 points. Currently, there are less than 100 active LRC addresses per day. This suggests that Loopring remains an immature product with little traction or interest from the wider crypto ecosystem.
As a DEX protocol, Loopring is dependant on incentive-driven ecosystem participants in the form of relayers. Without an active base of traders, relayers will likely not join, and vice versa if traders are not able to connect with a network of relayers. A network effect that would naturally improve UX and efficiency of the protocol is clearly not active at present.
The Loopring Foundation is trying to improve this situation with a new transaction fee model and incentive system.
As such, active addresses/network effects appear to have little impact on the value of LRC.
This suggests that most token holders are purchasing LRC as a speculative bet on future relevance, essentially buying at today’s prices as a call option on what they believe the Loopring protocol will be worth in the future.
Exchanges and trading pairs
The most popular trading option for LRC is USDT with the pair handling close to 57% of daily trading volumes. The second most popular market is the LRC/BTC pair. Together the top two pairs make up over 95% of the daily trading volume. The USD value of the daily volume of the entire LRC trading market is ~USD 1.9 Million. While fiat options for LRC do exist, they appear to be rarely used and illiquid.
A mix of exchanges make-up the LRC trading ecosystem. Markets on major exchanges, OKEx and Binance, operate the top two pairs in the ecosystem The LRC/USDT market is by far the busiest marketplace for LRC trading. SNT is also tradeable on large, prominent exchanges such as Bitfinex and Bittrex.
Technical analysis
Moving averages and price momentum
On the 1D chart, LRC has followed a negative linear price trend with a Pearson’s R correlation between time and price of ~0.80 (not shown), which has allowed a death cross to persist since 2018. However, since mid-December, LRC has seen a 75% surge, which has price currently sitting near $0.057. Unfortunately, despite the recent uptrend, price failed to break above the 200 day EMA (first arrow) and fell beneath the 50 day EMA (second arrow), which will now acts as resistance.
On the 1D chart, furthering the current bearish outlook, price current sits beneath the 0.382 Fibonacci retracement level, which acts as resistance. Both the 50 day EMA and 0.382 Fibonacci level offer resistance to price, which will only be overcome by a strong increase in buying volume.
Lastly, on the 1D chart, the volume flow indicator (VFI) is still strongly above 0 with a positive trend still intact, despite the recent price weakness. Price will need this buying momentum to maintain or increase in order to begin moving higher once again. An additional positive note is that, at the time of writing, LRC’s linear uptrend is still intact.
Ichimoku Clouds with Relative Strength Indicator (RSI)
The Ichimoku Cloud uses four metrics to determine if a trend exists; the current price in relation to the Cloud, the color of the Cloud (red for bearish, green for bullish), the Tenkan (T) and Kijun (K) cross, Lagging Span (Chikou), and Senkou Span (A & B).
The status of the current Cloud metrics on the 1D frame with singled settings (10/30/60/30) for quicker signals are bearish: price is below the Cloud, Cloud is bearish, the TK cross is bearish, and the Lagging Span is below Cloud and price.
A traditional long entry would occur with a price break above the Cloud, known as a Kumo breakout, with price holding above the Cloud. From there, the trader would use either the Tenkan, Kijun, or Senkou A as their trailing stop.
Price originally completed a Kumo breakout in early-April 2019, but has struggled ever since. Currently, price has fallen beneath the Cloud and currently sits at support near $0.056.
Currently, there are few positive factors for LRC, but some include:
- VFI is still in the bulls’ favor
- RSI is currently at a decent level of 36, which may reignite buying pressure.
As mentioned prior, buying volume will need to pick up demonstrably in order for LRC to re-complete a Kumo breakout above $0.085. In the event of a new breakout, price targets are $0.106 and $0.113. If price continues to drift lower, support levels are $0.05, $0.043, and $0.04.
The status of the current Cloud metrics on the 1D time frame with doubled settings (20/60/120/30) for more accurate signals is bearish: price is below the Cloud, Cloud is bearish, the TK cross is bearish, and the Lagging Span is below the Cloud and price.
The slower settings yield similar results with price currently sitting beneath the Cloud; including similar price targets and support levels.
Conclusion
The development of the Loopring protocol is impressive. The project continues to build its unique solution to the lack of liquidity on decentralized exchanges and DEX order matching challenges. The most recent update, Loopring 3.0 looks set to reduce fees and improve potential network scalability.
At a market level, however, the price of the token remains significantly down from previous bull market highs. The buying activity of LRC appears to be driven by speculators, with the on-chain value of the token a less pronounced driver of buying activity.

Don’t miss out – Find out more today